Plus: How RFID, NFC, and Bluetooth Differ and Work Together in IoT Solutions
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects countless devices and systems, enabling smarter automation, tracking, and data-driven decisions. Among the key enabling technologies are RFID, NFC, and Bluetooth — wireless communication methods that each play unique roles in IoT ecosystems. This article explains what RFID is, how it applies to IoT, and how it compares and integrates with NFC and Bluetooth technologies.
What is RFID?

RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. It uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a reader that emits radio waves and tags (either passive or active) that respond with stored information. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags do not require line-of-sight and can be read from a distance ranging from a few centimetres to over 100 metres depending on the type.
In IoT, RFID is widely used for inventory management, asset tracking, supply chain visibility, and access control. For example, retail stores use RFID tags on products to automate checkout and prevent theft, while logistics companies track shipments and pallets in real time.
RFID Made Simple: How It Works
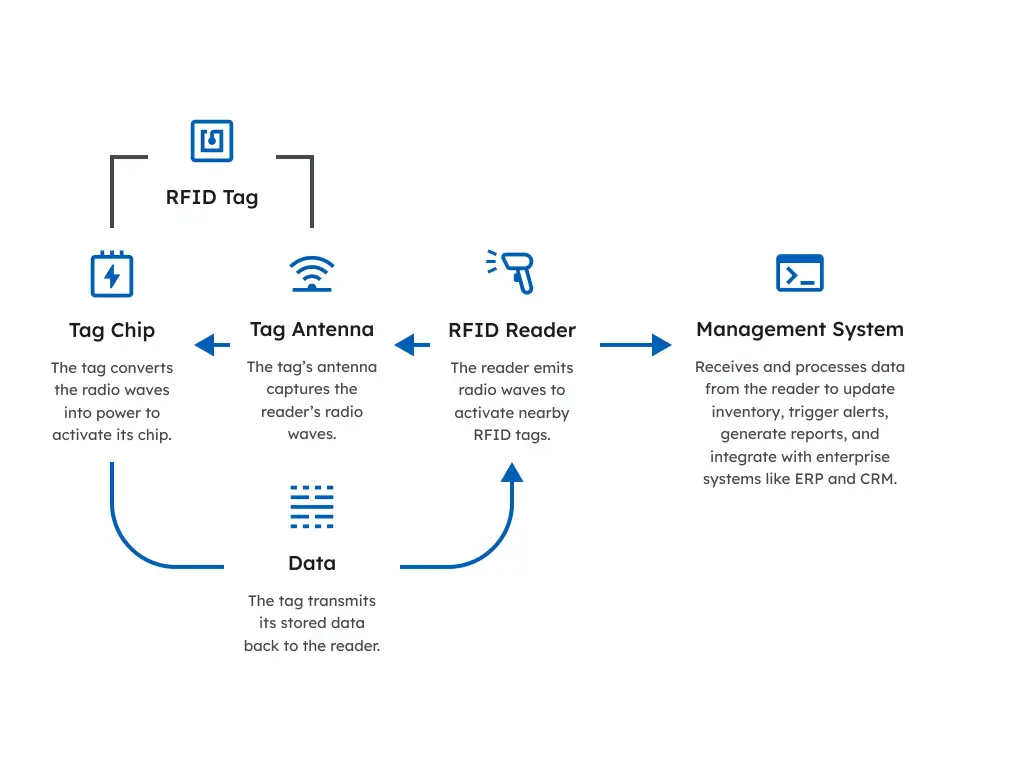
Think of RFID like a wireless barcode system — but better. Instead of needing to scan a barcode with a visible line of sight, RFID uses radio waves to identify objects without needing to see them directly. Imagine a supermarket checkout where items automatically register as you walk through a gate, without having to scan each barcode individually.
An RFID system has three main parts:
- Tags: Small chips attached to items that store information. Some tags have their own power source (active), while others get power from the reader’s signal (passive). Each tag contains a tiny antenna that captures radio waves from the reader.
- Reader: A device that sends out radio waves to “wake up” the tags and read their information.
- Antenna: Usually part of the reader, this device sends and receives radio signals over a certain range to communicate with the tags.
When the reader sends a radio signal, nearby tags respond with their stored data, allowing the system to quickly identify and track objects. This technology is widely used in retail, logistics, healthcare, and many other industries to save time and reduce errors.
Some RFID tags can only be read and cannot be changed (read-only), while others allow their stored data to be updated or rewritten by the reader (read-write). This means information on the tag can be modified as needed, which is useful for tracking changes or status updates.
What is NFC and How Does It Relate to RFID?

Near Field Communication (NFC) is a specialised subset of RFID technology standardised for very short-range communication (typically up to 4 cm). NFC operates at 13.56 MHz and allows two-way communication between devices, such as smartphones and contactless payment terminals.
Unlike general RFID, which often involves one-way communication from tag to reader, NFC supports peer-to-peer interactions, making it ideal for secure transactions, ticketing, and device pairing. NFC is also compatible with many passive RFID tags, enabling integration with existing RFID-based systems.
What is Bluetooth and How Does It Differ?
Bluetooth, specifically Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), is a wireless technology designed for medium-range (up to 100 metres) data exchange between devices. BLE is optimised for low power consumption, making it suitable for wearables, smart home devices, and IoT sensors that require frequent, short bursts of data transfer.
Unlike RFID and NFC, Bluetooth requires device pairing and supports higher data rates (up to 50 Mbps with Bluetooth 5.0). It is commonly used for continuous communication and control in IoT applications such as fitness trackers, smart locks, and environmental sensors.
Key Differences Between RFID, NFC, and Bluetooth
| Feature | RFID | NFC | Bluetooth (BLE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 125 kHz – 2.4 GHz | 13.56 MHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Range | Centimetres to 100+ metres | Up to 4 cm | Up to 100 metres |
| Data Rate | Low (varies) | Up to 424 kbps | Up to 50 Mbps |
| Power Consumption | Very low (passive tags) / moderate (active tags) | Very low | Moderate (optimised for low energy) |
| Communication | One-way (reader to tag) or two-way | Peer-to-peer, read / write, card emulation | Two-way, requires pairing |
| Security | Low to moderate | High (short range, encryption) | Moderate to high (encryption, pairing) |
| Cost | Low (passive tags) to moderate (active) | Moderate | Higher due to complexity |
| Typical Uses | Inventory, asset tracking, access control | Payments, ticketing, device pairing | Wearables, smart home, continuous data exchange |
How These Technologies Integrate into IoT Solutions
In modern IoT systems, RFID, NFC, and Bluetooth often complement each other to provide comprehensive connectivity and functionality:
- RFID is ideal for large-scale, cost-effective tracking of assets and inventory without manual scanning. It provides foundational data for supply chain transparency and automation.
- NFC adds secure, short-range communication for user interactions such as contactless payments, access control, and quick device pairing, enhancing user convenience and security.
- Bluetooth (BLE) enables continuous, medium-range communication for wearable health devices, environmental sensors, and smart home gadgets, supporting real-time monitoring and control.
For example, a smart logistics solution might use RFID tags to track packages in warehouses, NFC for secure access control at facilities, and Bluetooth sensors to monitor vehicle conditions and driver health. Together, these technologies create a layered, interconnected IoT ecosystem that enhances efficiency, security, and user experience.
RFID, NFC, and Bluetooth are fundamental wireless technologies driving the IoT revolution. Understanding their differences and how they integrate enables businesses to develop smarter, more effective IoT solutions tailored to their specific needs. Whether it’s tracking assets, facilitating secure payments, or connecting smart devices, these technologies form the backbone of a truly connected future.
At Howood International, we specialise in providing end-to-end IoT solutions that harness the power of RFID, NFC, and Bluetooth to enhance operational efficiency, security, and user experience. Get in touch with us to find out how our expertise can help your business unlock the full potential of IoT.



